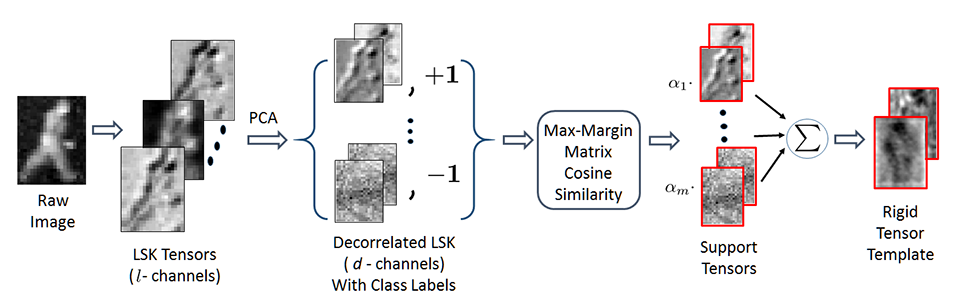
Max-Margin Matrix Cosine Similarity
See more details and examples in the following paper:
Sujoy Kumar Biswas, Peyman Milanfar, Linear Support Tensor Machine: Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Infrared Images, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017
LSK tensor descriptors are projected onto leading principal components to yield decorrelated and discriminatory feature tensors which are then used in a max-margin training framework with the matrix cosine similarity kernel. Owing to the linearity of the kernel, support vectors are combined into a rigid tensor detector for fast and efficient detection.

LSK Visualization: First column displays raw infarred images of pedestrians in different poses. HOG and LSK descriptors are displayed in grayscale (second and third column respectively) as well as in colormap (fourth and fifth column respectively). Columns sixth, seventh and eighth show LSK features after projecting the descriptors on three leading principal components.
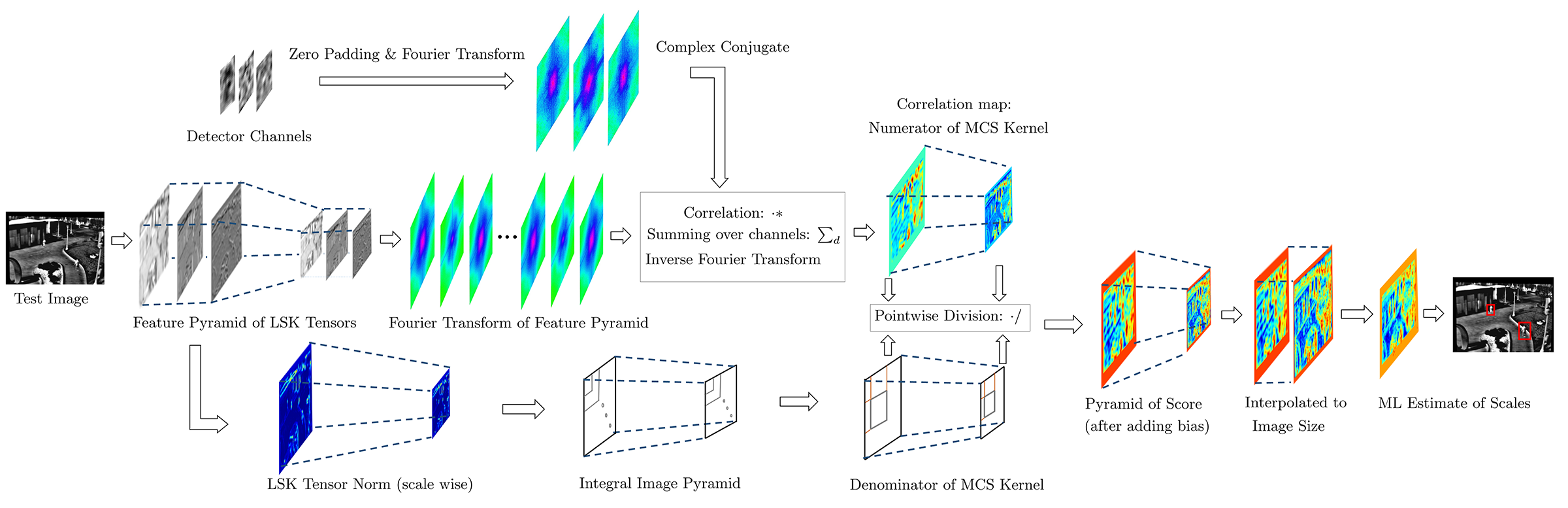
Faster Search: Multichannel Fourier transform and integral image facilitates exact acceleration of the decision rule.
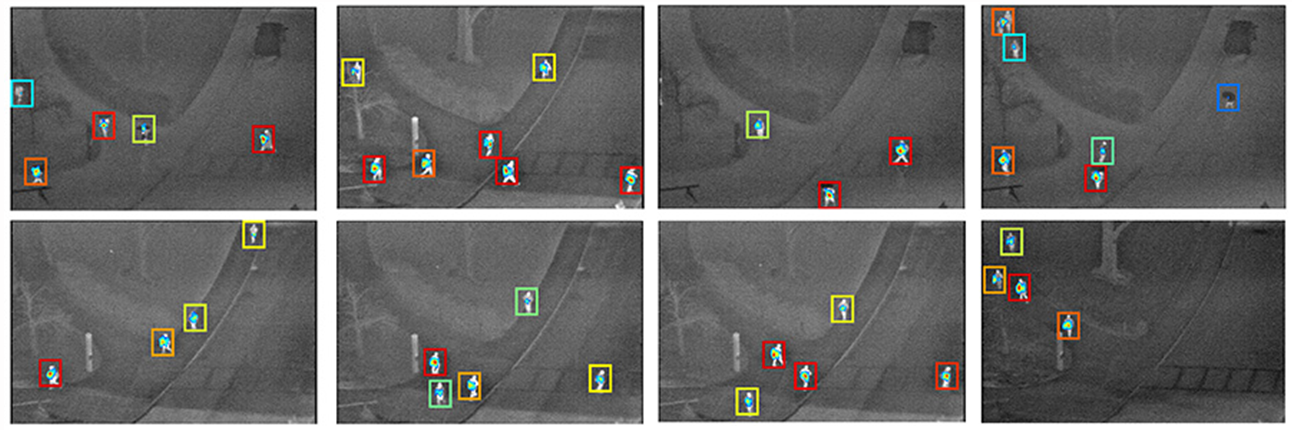
OSU Thermal Dataset [1] The detection scores above the threshold are embedded inside the displayed bounding box. The convention of color map is maintained, i.e., a red bounding box indicates highest confidence and blue bounding box lowest confidence
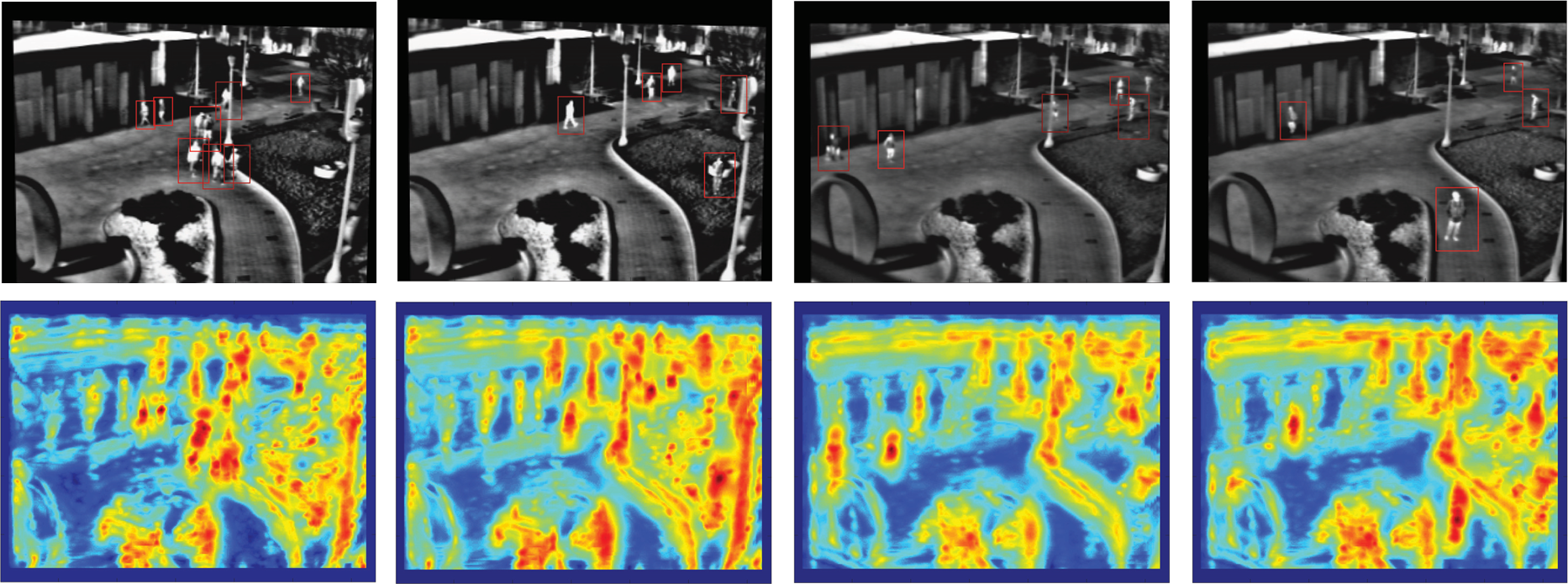
OSU Color Thermal Dataset [2] (only thermal channels are used) Top row shows multiscale detection on three frames from OSU-CT dataset. The scale best estimated is shown with the appropriate sized bounding box centered at the predicted location. The bottom row heat maps illustrate corresponding decision scores (maximum likelihood estimate across all six scales) obtained from the classifier. The blue regions show less confidence and the red to reddish black shows high to very high confidence in detecting pedestrians. Note we have not used any tracking information and/or background model.
Annotations We have annotated the thermal (and color channels as well) for all the sequences for our purpose. Note, the thermal and color image pairs are not registered. Hence, there exist separate annotation files. We have used Piotr Dollar's Computer Vision Toolbox [4-6] for the annotation. The annotation files will be available soon (meanwhile please contact the first author if you need them).
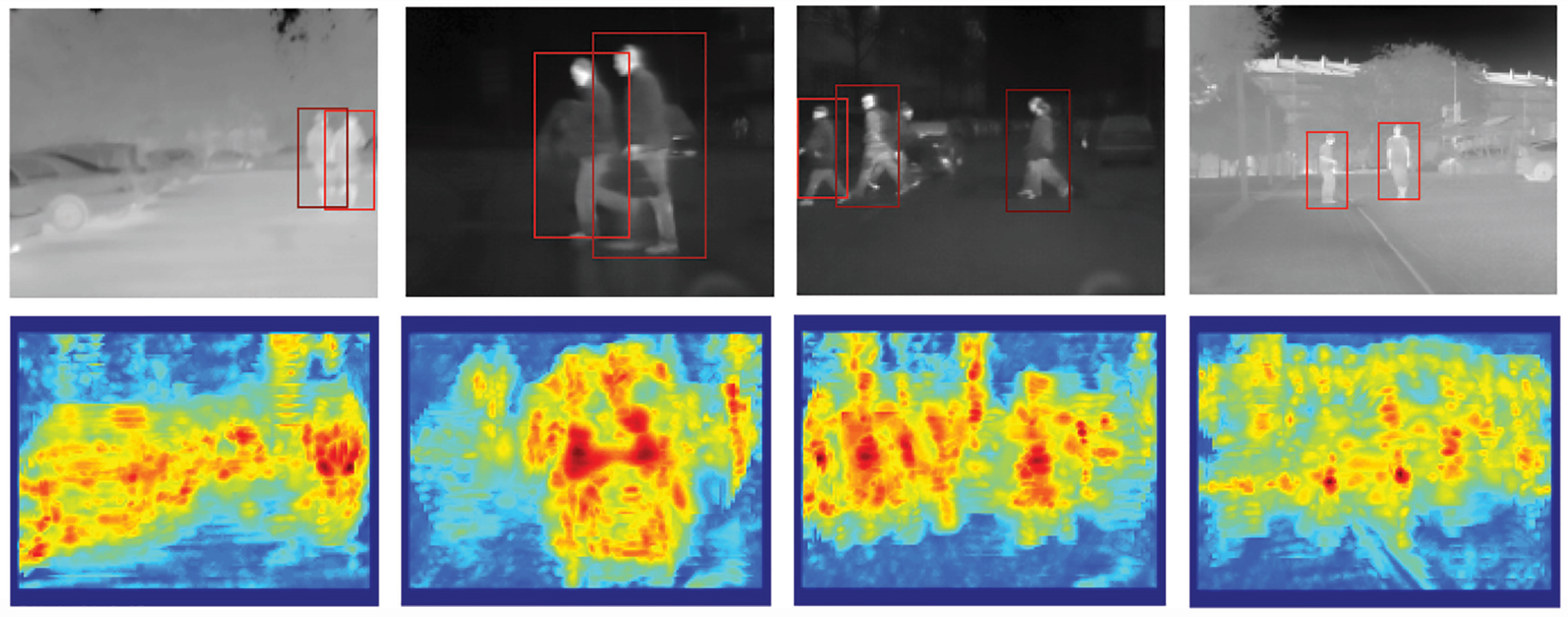
LSI thermal infrared dataset [3] Results show multiscale detection of pedestrians across wide range of scales. The estimated likelihood of pedestrian’s location measured across all the scales is shown under each frame. As before, the dark red to reddish black denotes high to very high confidence of the detector.
J. W. Davis and M. A. Keck, A two-stage template approach to person detection in thermal imagery, Proc. Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision. IEEE, 2005
J. W. Davis and V. Sharma, Background-subtraction using contour-based fusion of thermal and visible imagery, Computer Vision and Image Understanding, vol. 106, no. 2, pp. 162–182, 2007
D. Olmeda, C. Premebida, U. Nunes, J. Armingol, and A. Escalera, LSI far infrared pedestrian dataset, 2013
P. Dollár, C. Wojek, B. Schiele and P. Perona, Pedestrian Detection: An Evaluation of the State of the Art, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012
P. Dollár, C. Wojek, B. Schiele and P. Perona, Pedestrian Detection: A Benchmark, CVPR 2009
P. Dollár, Piotr's Computer Vision Matlab Toolbox (PMT), https://github.com/pdollar/toolbox
Representative implementation to visualize LSK channels and their PCA projections like Fig. 2 in the paper. The principal components sometimes swap their positions, especially on different machines, and the reason is not very clear to me. Download Zip
OSU Color Thermal Annotations in VBB format (Download Zip)
Full implementation of learning-prediction-evaluation on OSU thermal images (Download Zip)